React 解读
转载自掘金文章:React17 源码分析
author: xfz
19 版本特点
Actions
- useTransition
- useActionState
- useFormState
- useOptimistic
- use
React 19 新内容:React19 new content
以下所有案例,直接复制到 codesandbox 中运行即可,缺少的 import 请自行补充。
- Actions: useTransition 任务执行方法及状态
const updateName = () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
Math.random() > 0.5
? resolve("finished")
: reject(new Error("error get"));
}, 1000);
});
};
export default function App() {
const [name, setName] = useState("init");
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
const [isPending, startTransition] = useTransition();
const handleSubmit = () => {
startTransition(async () => {
const res = await updateName().catch((err) => setError(err));
res && setName(res);
});
};
return (
<div className="App">
<h1>Hello {name}</h1>
<h2>Start editing to see some magic happen!</h2>
<button onClick={handleSubmit} disabled={isPending}>
Update
</button>
{error && <p>{error.toString()}</p>}
</div>
);
}
const updateName = (name) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
Math.random() > 0.5
? resolve(`${name} finished`)
: reject(new Error("error get"));
}, 1000);
});
};
export default function App() {
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
const [state, submitAction, isPending] = useActionState(
async (previousState, formData) => {
setError(null);
const state = await updateName(formData.get("name")).catch((err) =>
setError(err)
);
if (state) {
return state;
}
},
null
);
return (
<form action={submitAction}>
<input name="name" />
<button type="submit" disabled={isPending}>
Update
</button>
<p>state: {state}</p>
{error && <p>{error.toString()}</p>}
</form>
);
}
function SubmitButton() {
const { pending } = useFormStatus();
return (
<div className="form_item">
<button className="primary" type="submit" disabled={pending}>
{pending ? "Submitting..." : "Submit"}
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default function App() {
const [state, submitAction, isPending] = useActionState(
async (previousState, formData) => {
const title = formData.get("name");
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
return [...(previousState || []), title];
},
null
);
return (
<form action={submitAction}>
<input type="text" name="name" />
<p>posts: {isPending ? "loading" : (state || []).join(",")}</p>
<SubmitButton />
</form>
);
}
const updateName = (name) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(`${name} finished`);
}, 1000);
});
};
function SubmitButton() {
const { pending } = useFormStatus();
return (
<div className="form_item">
<button className="primary" type="submit" disabled={pending}>
{pending ? "Submitting..." : "Submit"}
</button>
</div>
);
}
function ChangeName({ currentName, onUpdateName }) {
const [optimisticName, setOptimisticName] = useOptimistic(currentName);
const submitAction = async (formData) => {
const newName = formData.get("name");
setOptimisticName(newName);
const updatedName = await updateName(newName);
onUpdateName(updatedName);
};
return (
<form action={submitAction}>
<p>Your name is: {optimisticName}</p>
<p>
<label>Change Name:</label>
<input
type="text"
name="name"
disabled={currentName !== optimisticName}
/>
</p>
<SubmitButton />
</form>
);
}
export default function App() {
const [currentName, updateName] = useState("");
return <ChangeName currentName={currentName} onUpdateName={updateName} />;
}
使用 Promise 及 Context 示例
function Comments({ commentsPromise }) {
// `use` will suspend until the promise resolves.
const comments = use(commentsPromise);
return comments.map((comment) => <p key={comment.id}>{comment.comment}</p>);
}
function Page({ commentsPromise }) {
// When `use` suspends in Comments,
// this Suspense boundary will be shown.
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<Comments commentsPromise={commentsPromise} />
</Suspense>
);
}
const themeContext = createContext({ color: "light" });
export default function App() {
const theme = use(themeContext);
console.log("theme color:", theme?.color);
const commentsPromise = new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve([
{ id: 1, comment: "hello 1" },
{ id: 2, comment: "hello 2" },
{ id: 3, comment: "hello 3" },
{ id: 4, comment: "hello 4" },
]);
}, 1000);
});
return <Page commentsPromise={commentsPromise} />;
}
Improvements
移除了 forwardRef 的写法
function MyInput({placeholder, ref}) {
return <input placeholder={placeholder} ref={ref} />
}
//...
<MyInput ref={ref} />
Context 替代了 Context.Provider「已弃用」
const ThemeContext = createContext('');
function App({children}) {
return (
<ThemeContext value="dark">
{children}
</ThemeContext>
);
}
- Cleanup functions for refs
<input
ref={(ref) => {
// ref created
// NEW: return a cleanup function to reset
// the ref when element is removed from DOM.
return () => {
// ref cleanup
};
}}
/>
// 停止使用 隐式返回,因为引入了 ref 清理函数,需改为下面写法
- <div ref={current => (instance = current)} />
+ <div ref={current => {instance = current}} />
- useDeferredValue initial value
当提供 initialValue 时,useDeferredValue 会将其作为组件初始渲染的值返回,并使用返回的 deferredValue 在后台安排重新渲染。
function Search({deferredValue}) {
// 首次渲染的值为 空字符串
// 然后使用新得到的 deferredValue 安排重新渲染
const value = useDeferredValue(deferredValue, '');
return (
<Results query={value} />
);
}
15 版本特点
React 15 的架构分为两层
- Reconciler 协调器:用于收集需要更新的组件、patch Vnode 更新标识
- Renderer 渲染器:将变化后的组件进行 dom-diff => 渲染到页面上
15版本的reconciler 是 stack-reconciler。采用递归方式工作,同步进行,在生成虚拟dom树并diff的时候无法中断。
当组件层级过深时,会造成线程一直被占用,浏览器无法布局和绘制,造成丢帧、卡顿
16 版本特点
React 16 的架构分为三层
- Scheduler 调度器:调度任务的优先级,高优先级的优先进入 Reconciler 阶段
- Reconciler 协调器:收集需要更新的组件:fiber root 构建 - patch - Vnode 标识
- Renderer 渲染器:将变化后的组件进行 dom-diff => 渲染到页面上
17 版本特点
在 V16 版本中,以 expirationTime 的大小来衡量优先级,expirationTime 越大,则优先级越高,
但如果有一个高优先级异步 IO 任务(比如 Suspense,等待接口返回再执行后续操作)
和低优先级的任务(比如 cpu 任务),那么按照目前的模型,高优先级任务会始终阻塞低优先级任务
低优先级任务需要等待,直至高优先级 IO 任务执行完毕才会被执行,
这样是不合理的,如何更好的处理高优先级和低优先级任务?
使用 lanes 模型替代 expirationTime 模型
- lanes 优先级管理: 解决了从前的每次只能执行一个任务,到现在可以同时执行多个任务的能力
- lanes 指定一个连续的优先级区间,如果 update 的优先级在这个区间内,则将位于该区间内的任务生成对应的页面快照
- lanes 使用 31 位的二进制,其中每个 bit 被称为一个 lane,代表优先级;
- 某几个 lane 组成的二进制数被称为一个 lanes,代表一批优先级,这样 react 可以分别给 IO 任务、低优先级的任务分配不同的 lane,最后可以并发执行这几种类型的优先级
其本质是[叠加算法],多个任务可以叠加表示,用 JS 来表示就是一个状态队列 { lanes: [1, 2, 3] },
表示 fiber 有三个不同的优先级,他们应该被批处理
React 作者 acdlite 觉得操作状态队列不够方便,进而采用了一种"位运算代替状态队列"的方式:
{ lanes: 0b10010 }, 新的 lane 算法中, lanes 是一个二进制数,比如 10010 是由 10000 and 00010 两个任务叠加而成
Fiber 及相关源码处理 详见文章:Fiber详解
生命周期变更
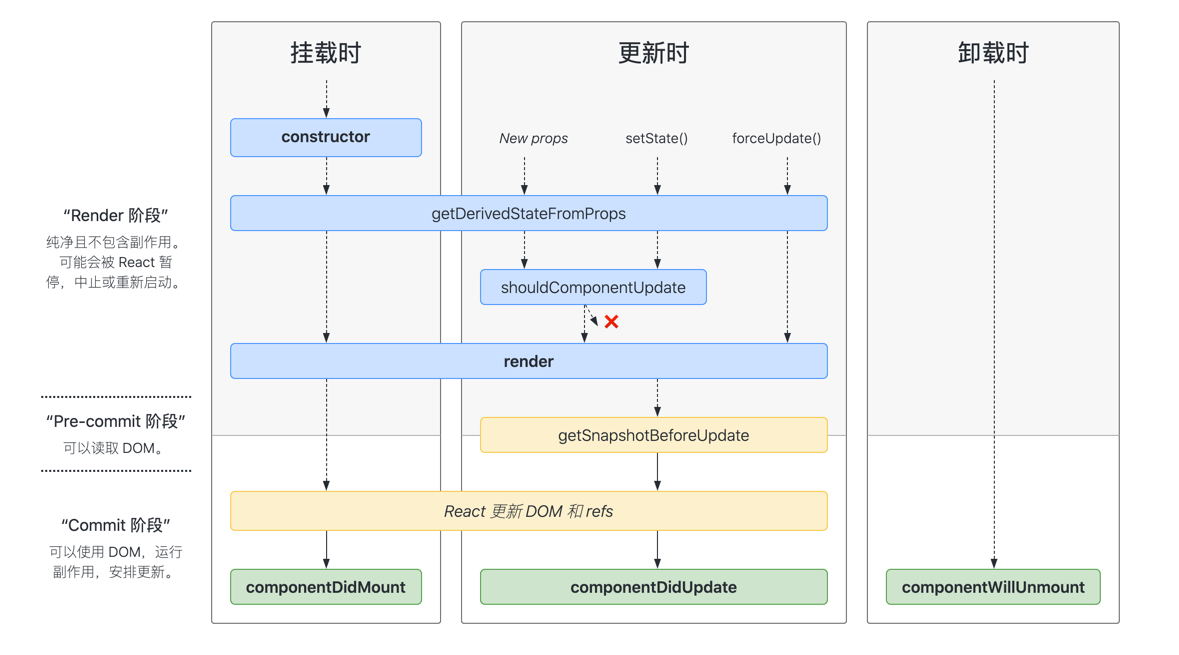
挂载阶段
- constructor
- static getDerivedStateFromProps
- render
- componentDidMount
更新阶段
- static getDerivedStateFromProps
- shouldComponentUpdate
- render
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
- componentDidUpdate
卸载阶段
错误处理
- static getDerivedStateFromError
- componentDidCatch
Hook 是什么?常用的 API,最佳实践
Fiber 是什么?
一次渲染流程
一次更新流程
源码解析

